When comparing grid computing vs cloud computing, grid computing is ideal for large-scale scientific research, where resources are pooled to solve complex problems. On the other hand, cloud computing provides scalable, on-demand services like infrastructure and software solutions, making it more flexible for everyday business needs and personal use
Grid Computing vs Cloud Computing
What is Grid Computing?
Grid computing is a distributed computing model where computing resources from different places are combined to solve a specific problem. It links unused resources of many computers to solve one big problem or a complicated one that cannot be solved by one computer alone. Often referred to as being conducted on a ‘data grid’, this system sees several computers working in tandem, and communicating directly with each other.
The Uses and Advantages of Grid Computing
Financial Services
Risk assessment difficulties are handled via grid computing in the spheres of financial institutions. Due to the use of the grid, they can decrease the time to predict the changes of the portfolio in the highly unpredictable markets.
Healthcare
The demand for handling large amounts of patient data leads to the healthcare sector using grid computing. This makes it possible to tailor treatment plans, fosters medical research and equally assists in the prevention and management of disease epidemics.
Media
In the media industry, grid computing enhances the generation of complex special effects in films. Currently, special effects designers apply grid-supported software in distributing the processing resources to accelerate the production
Gaming
It is also applied by game developers to obtain more processing capacity. Complex jobs like drawing graphics for a game are divided into several computers, and the developers can finish their work faster.
Life Science
The application of grid computing is growing constantly in the life sciences, P4 medicine, bioinformatics and computational biology. It allows practitioners to search, collect and analyze pertinent information, perform massive, realistic and fast modeling and run remote devices as a part of the current healthcare framework.
What is Cloud Computing?
It is a way of using the internet to convey services such as “servers”, “storage”, “databases”, “networking”, “software” and “analysis”. Public and private businesses of all sizes employ cloud computing to save information and access it using the internet connection.
Use Cases and Applications of Cloud Computing
Testing and Development
Cloud computing flexibility enables the setup of systems/settings, testing, and tearing down in the shortest time possible. New environments can be set up in minutes as opposed to long periods that are required by conventional solutions. This increases the speed at which organizations bring new products into the market and also increases efficiency.
Big Data Analytics
Cloud computing leverages the computational capability required in big data analysis which in turn provides organizations with vital information to make the right decisions and improve operations.
Big Data Insights
Big data as a service enables businesses such as Facebook and Amazon to gather information on customers’ preferences, purchase intentions and other parameters using data analytics with the help of cloud computing. This information helps to forecast future consumption; promotes the company’s development.
Email Services
Most are web-based, known as Software as a Service (SaaS), and are essential in the daily functioning of administrations across industries and functions such as sales, marketing and IT. Cloud accessibility guarantees that email services are credible and can be accessed from any place.
Infrastructure Services
Management of IT infrastructure requires capital investment in the form of equipment, power consumption and other expenses. Businesses prefer to outsource their data to the service provider’s data centers which transform Capex into Opex; assisting them to concentrate on their core business activities.
Grid Computing and cloud computing have different advantages of distributed computing. Grid is good at concentrating resources for large-scale problems and the cloud provides ‘pay as you go’ flexibility. They can integrate in the future, where cloud platforms control the grid resources or new security technologies allow for the mix. They could also turn into rivals where cloud providers build their own tools or grid changes to include on-demand systems. This will be dictated more by the user requirements and technological evolution; is an interesting area to track as distributed computing paves the way to the future.
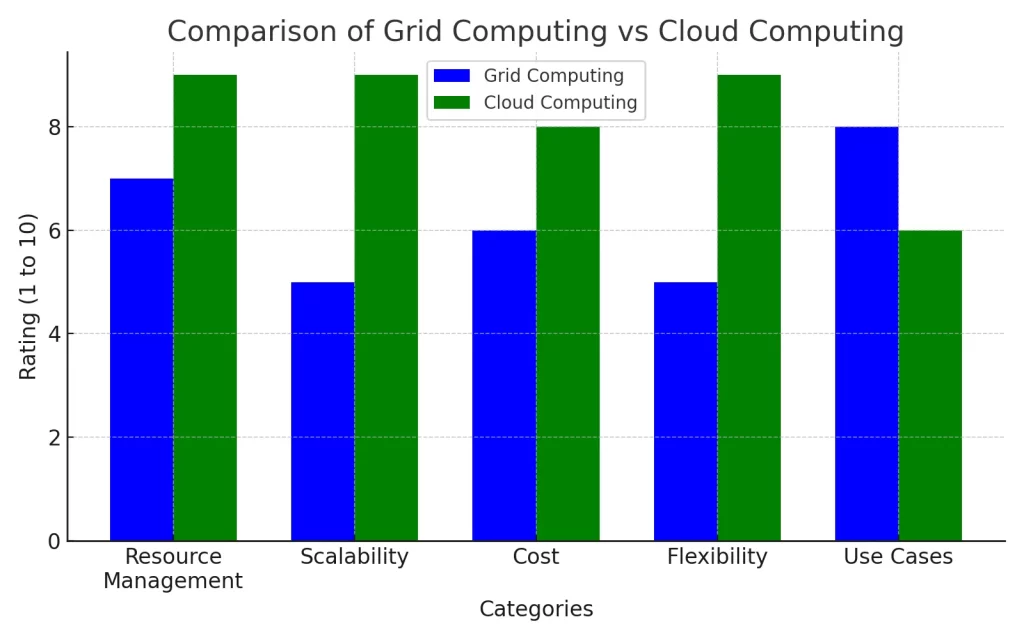
In Below Graph Comparison Of Grid Computing Vs Cloud Computing based on key aspects like resource management, scalability, and cost.


Leave a Comment