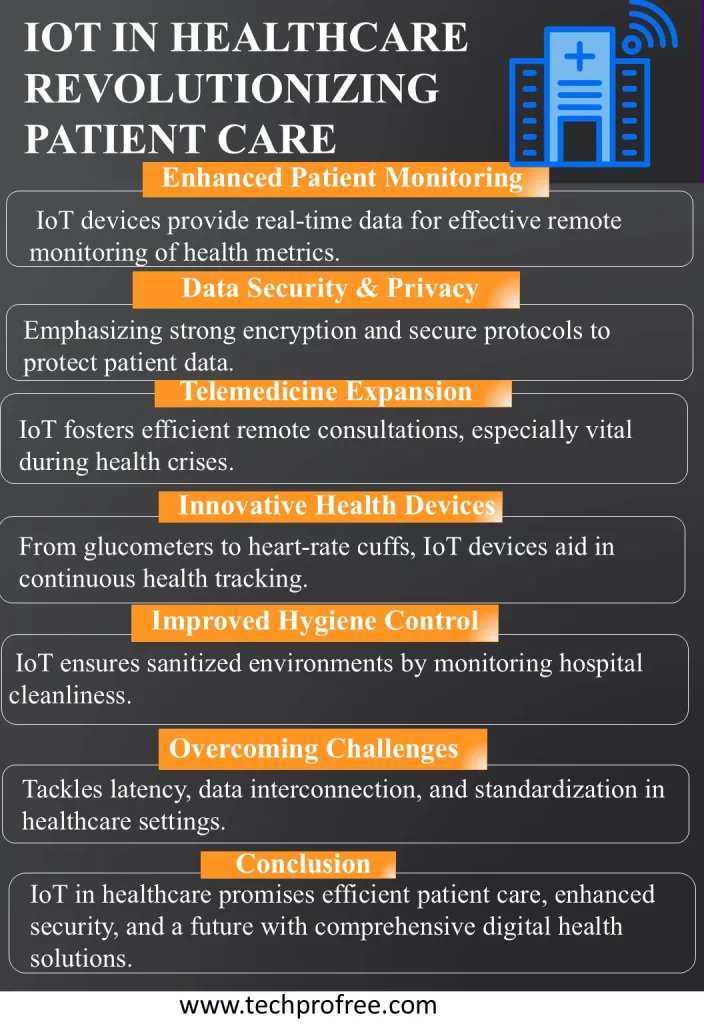
IoT in Healthcare Making Big News in current Era Traditionally, communication with healthcare personnel was mainly face-to-face, over the phone, and through written messages. This was equally alarming to doctors as it disrupted the continuity of patient’s health checkups and timely advice.
In general, the concept of IoT offers immense possibilities to optimize the results, minimize expenditures and increase the effectiveness of the work in the sphere of healthcare. The COVID-19 pandemic has increased the usage of telemedicine technologies that are now considered effective solutions for providing quality care. The previous technological challenges have been tackled by healthcare providers resulting in enhanced achievements through connected devices.
The incorporation of IoT in the healthcare system has brought about very developed systems that address the requirements of medical facilities. Sensors have been integrated into IoT frameworks in a more significant number, giving unprecedented connectivity and operation intelligence. These sensors are the latest modern development of technology that has recently changed the practices of healthcare for the better cure to the increased potential for accurate and efficient tracking and handling of patients.
Challenges of IoT in Healthcare Industry
Multiple major concerns have to be solved to optimize the usage of IoT technology in the sphere of healthcare.
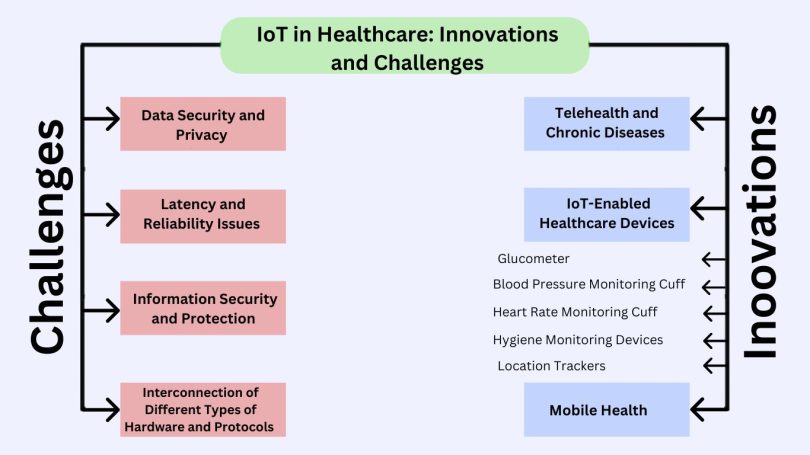
Data Security and Privacy
One of the main public concerns based on IoT in healthcare is the management of personal information from the medical records through the Internet thus posing a major threat to security. Hence, the protection of this valuable information is very important. Thus, the developers of IoT solutions for healthcare should consider the following threats and remember that the proper communication protocols, data encryption, and secured back-end systems should be used to prevent these threats effectively.
Latency and Reliability Issues
Another significant concern is the latency in the data transfer especially in cases where any delay can be deadly. Emphasizing the issue of low latency and high reliability through suitable communication protocols is crucial. Hence, solutions that offer high security and fast response times are needed to tackle such challenges.
Information Security and Protection
The constant transmitting and logging of data by IoT security devices are a major privacy and security concern. Today, there are no specific standards for the usage of data in IoT devices, and security protocols in devices are not well specified. The absence of clear definitions and laws in this area creates an easy opportunity for hackers to gain unauthorized access and steal Personal Health Information (PHI) belonging to patients and healthcare providers. The latter can be bought and resold or used to fabricate identification documents, procure and sell medicines and medical equipment and other products, including submitting fraudulent compensation claims.
Interconnection of Different Types of Hardware and Protocols:
IoT in the healthcare context is not only complex by the nature of the devices and their connectivity but also by the integration of multiple devices with different standards and communication protocols. Such non-standardization of devices complicates the process of data flow and becomes one of the main factors that prevent the widespread use of IoT in healthcare. The integration of protocols that are not well standardized frustrates the speed of the connected devices making IoT solutions less effective.
IoT has been widely implemented in the healthcare sector due to its benefits that has been acknowledged by both the hospitals and patients. Analyses predict that the market for healthcare IoT will be worth USD 446.5 billion dollars by 2028.
Innovations of IoT in Healthcare
These are the ways through which IoT is transforming the health sector as follows.
Telehealth and Chronic Diseases
The greatest opportunity of IoT in the healthcare sector is the ability to offer constant remote observation of the patient. The use of IoT corresponds with the popularity of mobile, internet-connected devices among patients, which means that they do not require a great amount of training to incorporate new solutions into their everyday routines.
IoT-Enabled Healthcare Devices
Several IoT-enabled devices are enhancing healthcare delivery…
Glucometer
New-generation glucometers integrated with IoT are capable of collecting data automatically and more frequently than traditional glucometers.
Blood Pressure Monitoring Cuff
Smart cuffs used for the monitoring of blood pressure can do the check-ups in real-time and do not need frequent visits.
Heart Rate Monitoring Cuff
These devices provide a consistent, long-distance monitoring of the heart rates taking into consideration the patient’s physical activity, medications and psychological condition.
Hygiene Monitoring Devices
Smart hygiene control by IoT makes sure that the surfaces in the hospital do not pose any health hazards due to infection.
Location Trackers
Small connected devices with geolocation features assist the hospitals in inventory management, asset tracking and locating equipment.
Mobile Health
Mobile health entails the use of mobile devices in the assessment and management of a patient’s health. It mainly ascertains useful in developing nations where people use smartphones, and may not access proper healthcare centers.
These technologies can include controlling medical monitoring equipment, health management applications, applications for reviewing medical data, exercise patterns, the management of other IoT devices, and doctor appointments. These applications can be useful for governments that seek to understand the trends in the population’s health.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT and healthcare promises a future that is filled with great potential. As far as the range of its applications is concerned, it is a technology that could revolutionize the healthcare sector from chronic disease monitoring to efficient working. Yet, data security or protection, compatibility of the device and clear regulations should be addressed. Engagement of all the stakeholders in the healthcare sector, including the healthcare service providers, technology developers, and regulatory bodies is a critical factor for entrenching security, setting up of data standards, and encouraging innovation. Conquering these obstacles allows for a new age of disease remote monitoring, robotic surgery aid, and medication adherence, leading to a healthier and more independent society.



Leave a Comment